CSS - Introducing Flexbox Layout
Information drawn from
The Flexbox Layout (Flexible Box) module
A W3C Candidate Recommendation as of October 2017, it aims at providing a more efficient way to lay out, align and distribute space among items in a container, even when their size is unknown and/or dynamic (thus the word “flex”).
The main idea behind the flex layout is to give the container the ability to alter its items width/height (and order) to best fill the available space (mostly to accommodate to all kind of display devices and screen sizes). A flex container expands items to fill available free space or shrinks them to prevent overflow.
Most importantly, the flexbox layout is direction-agnostic as opposed to the regular layouts (block which is vertically-based and inline which is horizontally-based). While those work well for pages, they lack flexibility (no pun intended) to support large or complex applications (especially when it comes to orientation changing, resizing, stretching, shrinking, etc.).
Note: Flexbox layout is most appropriate to the components of an application, and small-scale layouts, while the Grid layout is intended for larger scale layouts.
Basics
Since flexbox is a whole module and not a single property, it involves a lot of things including its whole set of properties. Some of them are meant to be set on the container (parent element, known as “flex container”) whereas the others are meant to be set on the children (said “flex items”).
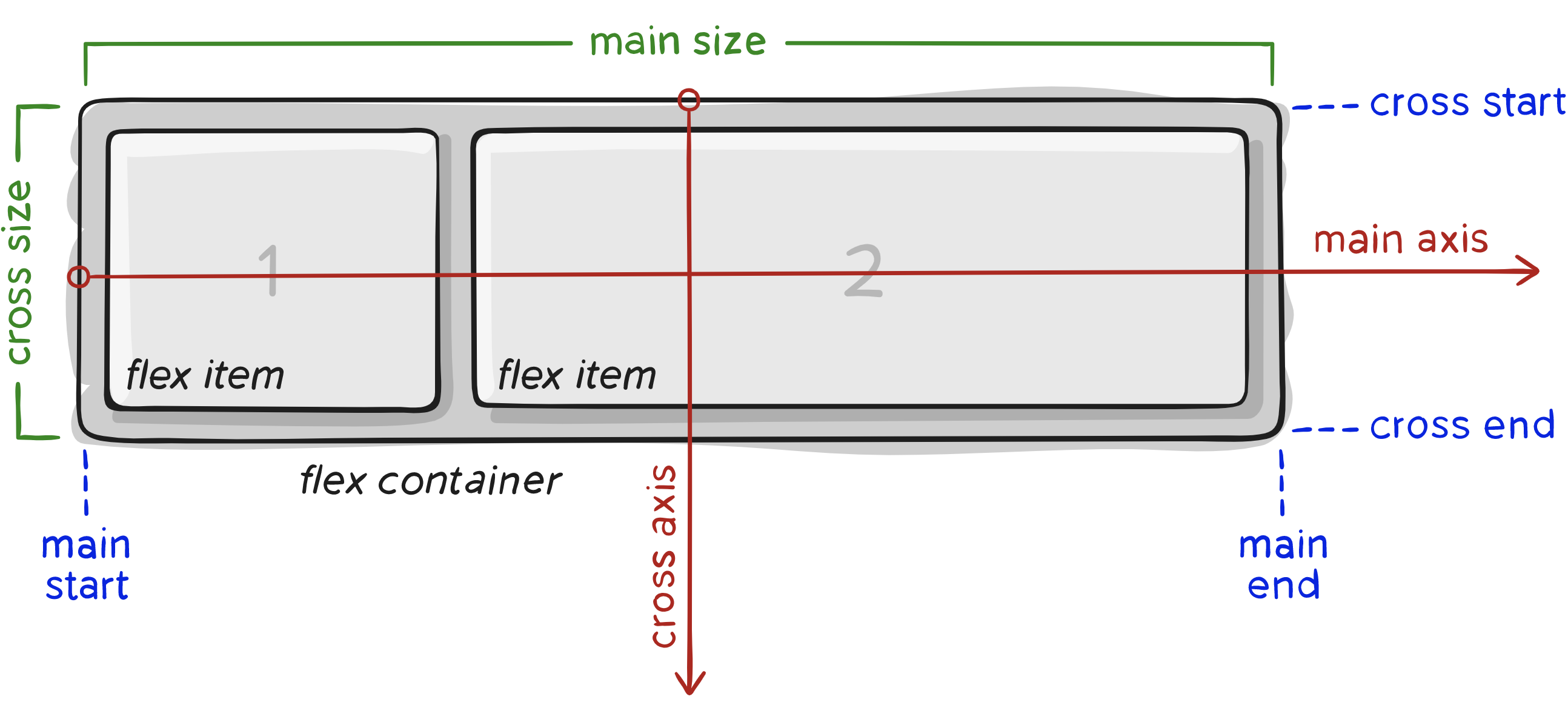
If “regular” layout is based on both block and inline flow directions, the flex layout is based on “flex-flow directions”. Please have a look at this figure from the specification, explaining the main idea behind the flex layout.

Items will be laid out following either the main axis (from main-start to main-end) or the cross axis (from cross-start to cross-end).
- main axis: The main axis of a flex container is the primary axis along which flex items are laid out. Beware, it is not necessarily horizontal; it depends on the flex-direction property (see below).
-
**main-start main-end** - The flex items are placed within the container starting from main-start and going to main-end. - main size - A flex item’s width or height, whichever is in the main dimension, is the item’s main size. The flex item’s main size property is either the ‘width’ or ‘height’ property, whichever is in the main dimension.
- cross axis - The axis perpendicular to the main axis is called the cross axis. Its direction depends on the main axis direction.
-
**cross-start cross-end** - Flex lines are filled with items and placed into the container starting on the cross-start side of the flex container and going toward the cross-end side. - cross size - The width or height of a flex item, whichever is in the cross dimension, is the item’s cross size. The cross size property is whichever of ‘width’ or ‘height’ that is in the cross dimension.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Last update on 23 Jan 2020
---